Discover the artistic legacy of Roy Lichtenstein, a pioneering figure in the Pop Art movement of the 1960s. From his iconic use of comic strip imagery to his innovative techniques, delve into 11 key aspects of Lichtenstein’s life and work, exploring his influence, themes, and lasting impact on the art world.
1. Pioneer of Pop Art: Roy Lichtenstein was a leading figure in the Pop Art movement of the 1960s, alongside artists like Andy Warhol. Pop Art celebrated elements of popular culture, often using techniques like comic book-style imagery and bold colors.
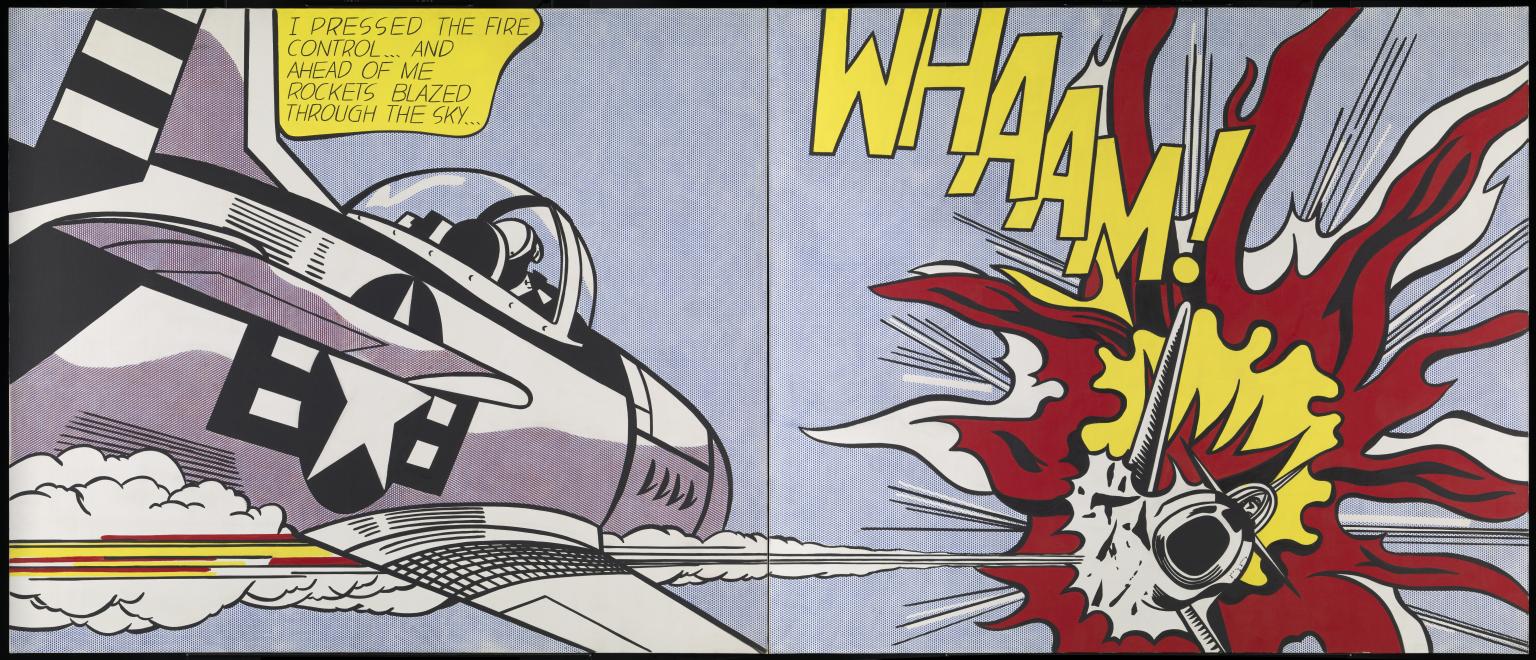
2. Whaam!: One of Lichtenstein’s most iconic works is “Whaam!”, created in 1963. It depicts an intense, dramatic scene inspired by comic book panels, featuring a fighter jet firing a missile with the onomatopoeic sound “Whaam!” in bold letters.
3. Ben-Day Dots Technique: Lichtenstein’s signature style often involved the use of Ben-Day dots, a printing technique used in comic books to create shading and colour variations. He replicated this effect in his paintings using stencils and a meticulous process.

4. Influence of Popular Culture: Lichtenstein drew inspiration from everyday imagery found in advertisements, comic strips, and consumer products. He transformed these mundane subjects into high art, challenging traditional notions of what constituted fine art.
5. “Look Mickey”: Another seminal work by Lichtenstein is “Look Mickey” (1961), which is considered one of the earliest examples of Pop Art. It features Mickey Mouse and Donald Duck in a humorous scene, rendered in Lichtenstein’s distinctive style.

6. Critique of Consumerism: Through his art, Lichtenstein explored themes of consumerism, mass production, and the saturation of media in society. His works often reflect the pervasive influence of advertising and popular culture on contemporary life.
7. Parody and Irony: Lichtenstein’s paintings often contain elements of parody and irony, challenging viewers to reconsider the significance of mass-produced imagery and the boundaries between high and low culture.
8. Commercial Success: Despite initial skepticism from the art world, Lichtenstein’s work gained widespread acclaim and commercial success. His paintings became highly sought-after, fetching significant prices at auctions and cementing his status as a major artist of the 20th century.
9. Artistic Process: Lichtenstein’s meticulous approach to painting involved careful planning and execution. He would often begin with sketches and studies before transferring the design onto a canvas, meticulously reproducing the details of his source material.
10. Legacy: Lichtenstein’s influence extends beyond the realm of visual art, impacting popular culture and inspiring subsequent generations of artists. His bold, graphic style continues to resonate with audiences around the world, cementing his legacy as a master of Pop Art.
11. Exhibitions and Recognition: Lichtenstein’s work has been exhibited in major museums and galleries worldwide, including retrospectives at the Museum of Modern Art in New York and the Tate Modern in London. He received numerous awards and honours throughout his career, solidifying his place in art history.
Feature Image Courtesy: Bill Ray via Gagosian.com
Controversy Surrounding Roy Lichtenstein’s Art Appropriation






