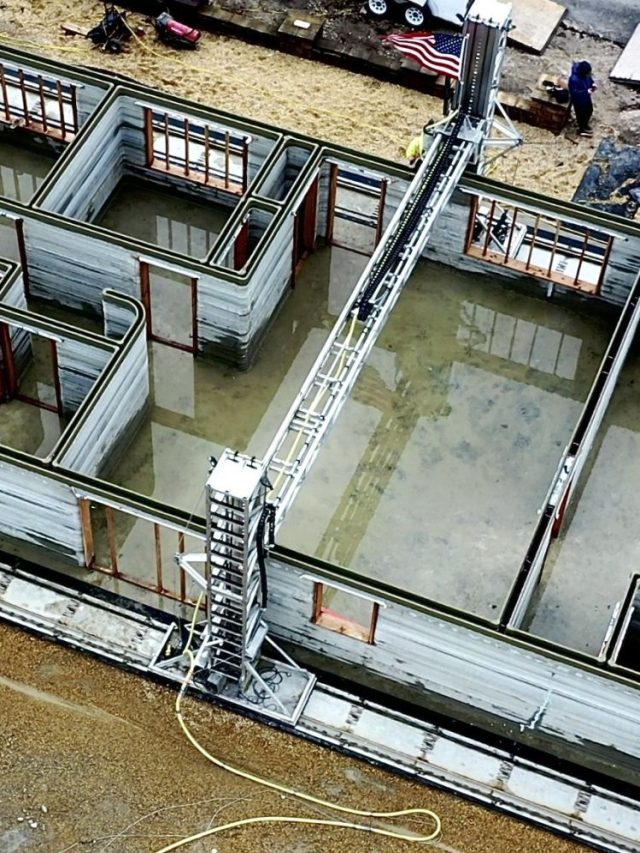
Implementing 3D Printing in Architecture
With additive manufacturing or 3D printing, expected to transform conventional building techniques, the construction sector is prepared for an upheaval in technology. This technique might lead to much shorter building timetables, less wasteful use of materials, and previously unheard-of design freedom. As Prof. Suhas Ramachandra points out in his Hindustan Times piece, complex architectural forms that were previously thought to be impossible to create using traditional construction methods may now be created thanks to 3D printing.
The process of 3D printing in architecture entails creating a digital blueprint using computer-aided design (CAD) software and then converting it into a format that 3D printers can read. This usually has to do with .STL or .OBJ files. When the design is complete, the digital blueprint is used by the 3D printer to precisely deposit layers of material, such as composites or concrete, to start building. One layer at a time, each solidifying before the next is added, creating a carefully built structure.
Benefits of 3D Printing in Architecture
There are several benefits to 3D printing in the architecture and construction sector. The method reduces material waste, opens up previously unattainable design flexibility, and significantly shortens building schedules. Furthermore, it makes it easier to create intricate architectural forms that were previously difficult to achieve via conventional techniques. The intrinsic layer-by-layer method allows for exact control over the distribution of materials, resulting in extremely strong and effective structures.
3D Printing a Building: How Does it Work?
There are various important processes involved in the 3D printing of a building process.
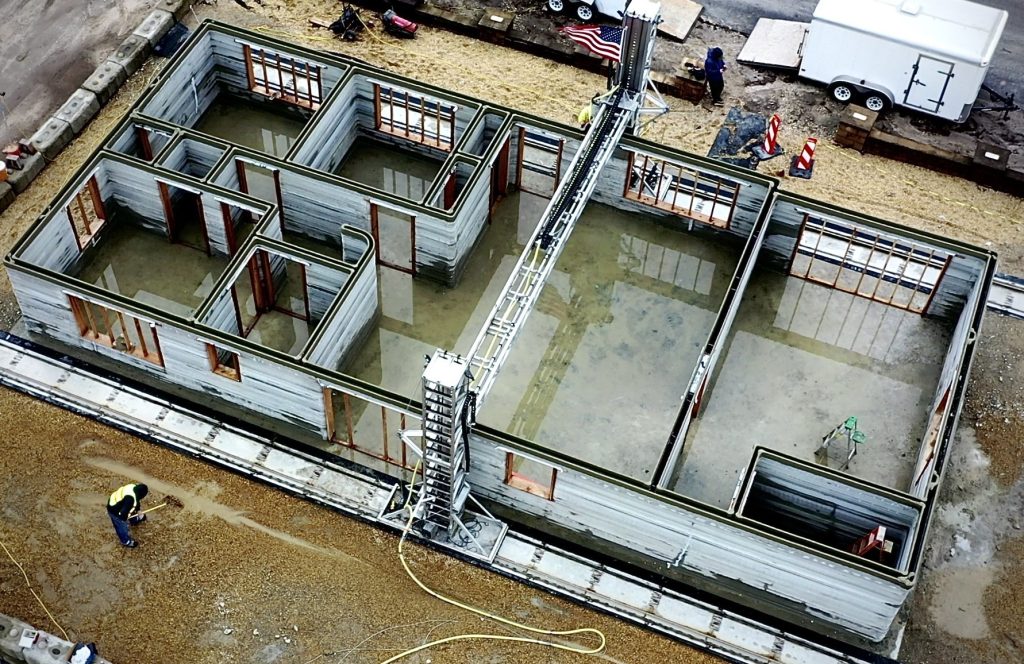

- The 3D printer’s blueprint is created digitally during the first design phase using specialist CAD software.
- The next stage is to choose the material, and concrete is a popular option because it is inexpensive, long-lasting, and suitable for layer-by-layer deposition. To increase the options for building projects, other materials such as polymers, composites, and recycled materials are also being investigated.
- Following the instructions on the digital model, the 3D printer carefully applies selected materials layer by layer during the printing process.
- It is essential to use the right curing techniques, such as heat application, chemical reactions, or UV light exposure, to guarantee the strength and structural integrity of the printed components.
- To improve the finished product, post-processing procedures can be required. These could include adding conventional building components like windows and doors.
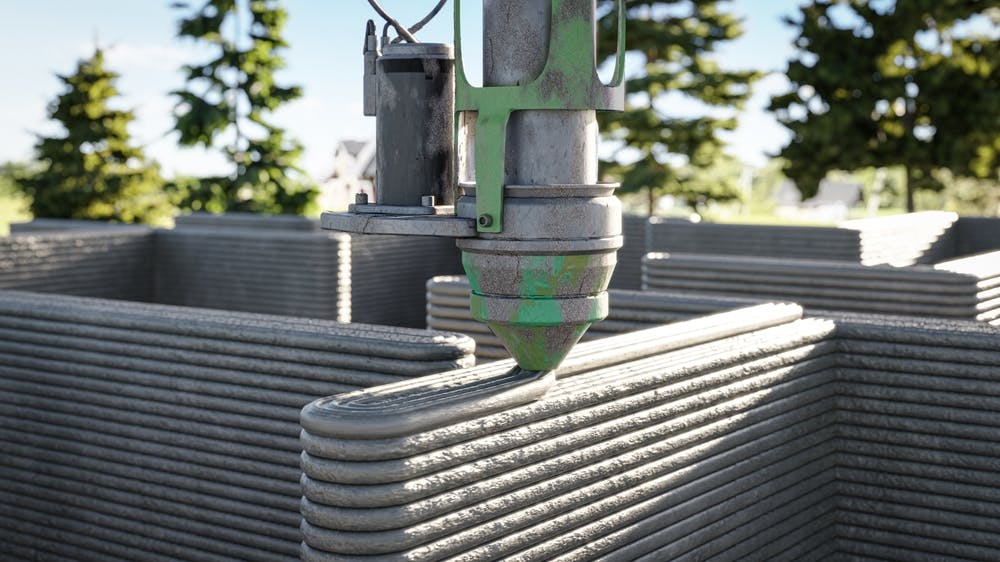
3D Printing in Architecture: Events
Advances in 3D printing and associated architectural and construction technologies were demonstrated at an event titled “Concrete Panorama & Seminar – 2023,” which was arranged by the Indian Concrete Institute in Bengaluru. Researchers, beginners, and professionals in the business came together on this forum to discuss the potential of cutting-edge construction techniques. Cutting-edge innovations, such as robotic construction, sophisticated formwork systems, sustainable materials, and smart building technologies, were showcased in live demonstrations. These gave viewers important insights into how the construction industry is changing quickly.

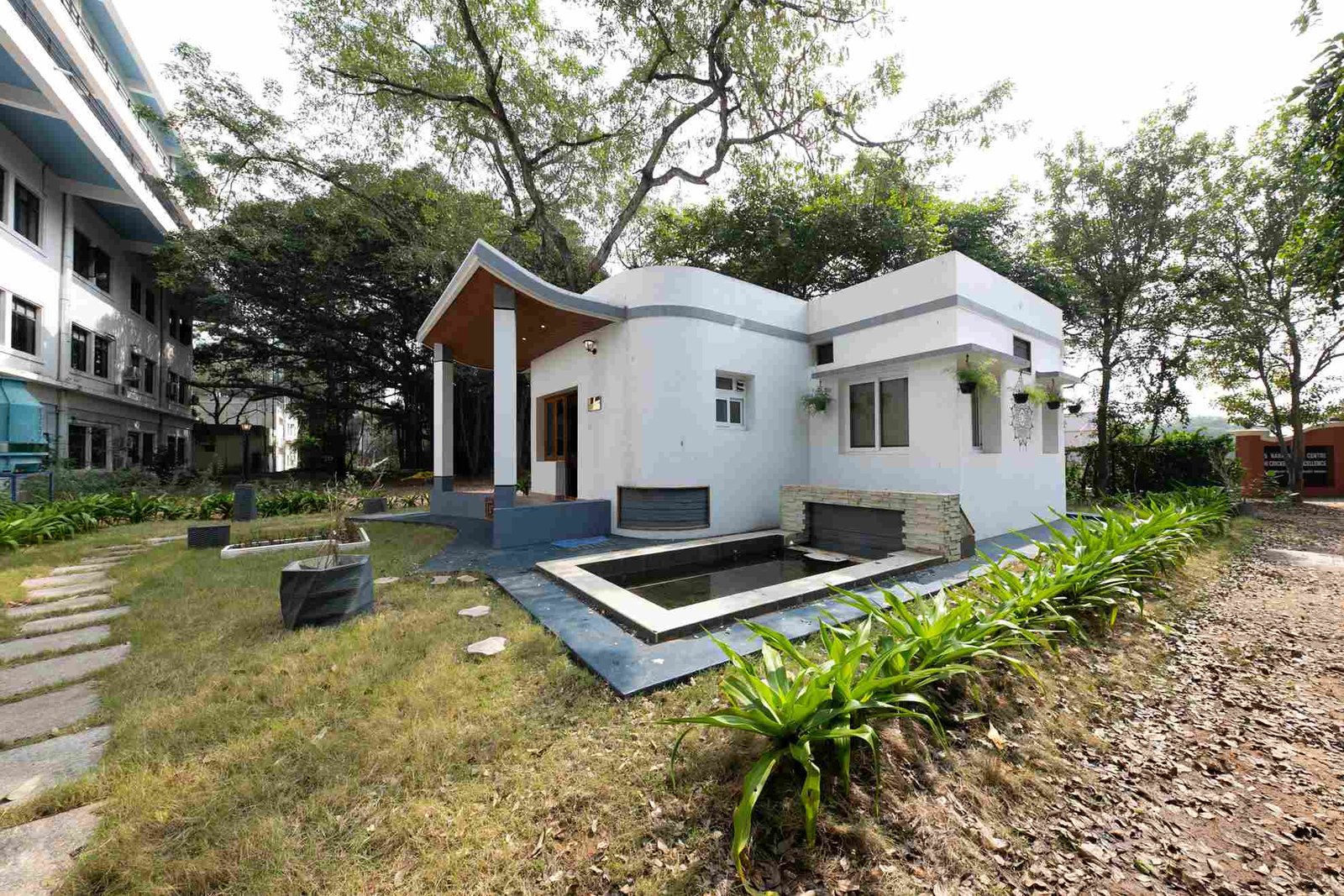
Instances of 3D Printed Technology Used in Indian Architecture
Following are some instances of 3D Printed Buildings in India
1. Godrej Bus Stands: The first 3D-printed bus stop in the country was built by Mumbai-based Godrej & Boyce, who assembled the modules in just one week. It uses 30% Recycled Concrete Aggregates (RCA) from concrete waste and includes independent solar panels.

2. Indian Air Force Sanitary Blocks: In Jaisalmer, sturdy sanitary blocks were built for the Indian Air Force. The Thar desert’s sand dunes served as inspiration for the project’s design.

3. IIT-M: The 500-square-foot “proof of concept” house was completed in 21 days after being modularly printed in Chennai. It was unveiled by Hon. Finance Minister Ms. Nirmala Sitharaman.

The use of 3D printing in the architecture and construction sector creates opportunities for ground-breaking innovations. Complete buildings, like as homes and workplaces, can be quickly and affordably built. More people can access prototyping, which makes it possible to see suggested structures more rapidly. Speedy production of architectural models enables clients to see their concepts come to life. Furthermore, building firms can create customized components with 3D printing, guaranteeing accurate dimensions and reducing waste.
Image Courtesy – Parametric Architecture






